Theoretical Investigation of Hydrogen Storage Ability of a Carbon Nanohorn
슈퍼관리자
2021-05-21
Theoretical Investigation of Hydrogen Storage Ability of a Carbon Nanohorn
-
Authors :
G. Chen, Q. Peng, H. Mizuseki, and Y. Kawazoe
-
Journal :
Comput. Mater. Sci.
-
Vol :
49
-
Page :
S378-S382
-
Year :
2010
Abstract
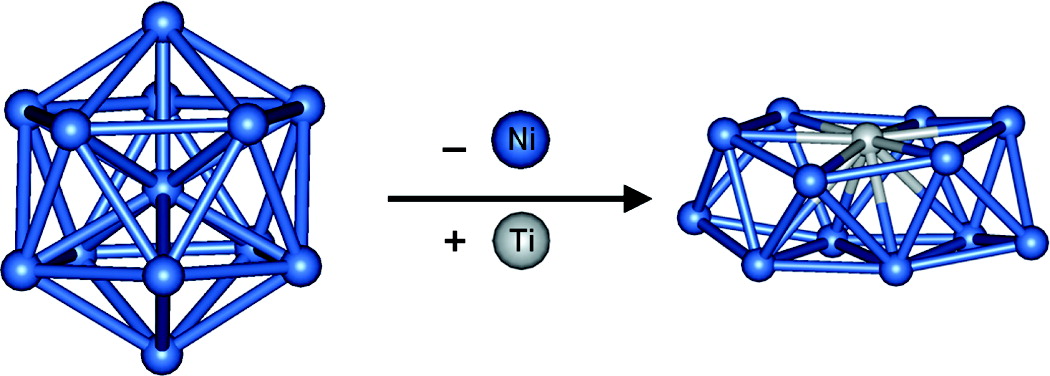
Using the first principles method, we study the growth behavior and electronic and magnetic properties ofTiNin (n ) 1-12) clusters to clarify the effect of Ti modulation on the nickel nanostructures. Furthermore,
chemisorption of H2 was studied to understand the chemical reactivity of H2 on the small Ni- and Ti-doped
Ni clusters. The calculations are performed using the plane wave pseudopotential approach under the density
functional theory and generalized gradient approximation for the exchange and correlation functional. The
optimized geometries of TiNin-1 clusters indicate that the substitution of Ti brings a substantial structural
reconstruction from 3D structure to a layer structure in which Ti atom is found to coordinate with Ni atoms
to a maximum extent. This is accompanied by a significant enhancement in binding energies and reduction
in chemical reactivity. Furthermore, the magnetic moments of the small Ti-doped Ni clusters are quenched
because of the antiferromagnetic alignment of the Ti electrons. The lowest-energy structure of H2 chemisorbed
on Ni clusters shows that hydrogen prefers to adsorb on the edge site with two hydrogen atoms on these
clusters in neighboring sites as the preferred arrangement. The incorporation of Ti atom improves the
chemisorption energy of Ni clusters. Bader charge analysis indicates that with the formation of metal hydride,
the H atoms withdraw charges from the metal centers, making them lose an electron, and carry a positive
charge over them. Furthermore, Ti doping is found to enhance the chemical reactivity of Ni clusters.