An Atomistic Level Description of Guest Molecule Effect on the Formation of Hydrate Crystal Nuclei by Ab Initio Calculations
슈퍼관리자
2021-05-21
An Atomistic Level Description of Guest Molecule Effect on the Formation of Hydrate Crystal Nuclei by Ab Initio Calculations
-
Authors :
R. V. Belosludov, H. Mizuseki, M. Souissi, Y. Kawazoe, J. Kudoh, O. S. Subbotin, T. Adamova, and V. R. Belosludov
-
Journal :
J. Str. Chem.
-
Vol :
53
-
Page :
619-626
-
Year :
2012
Abstract
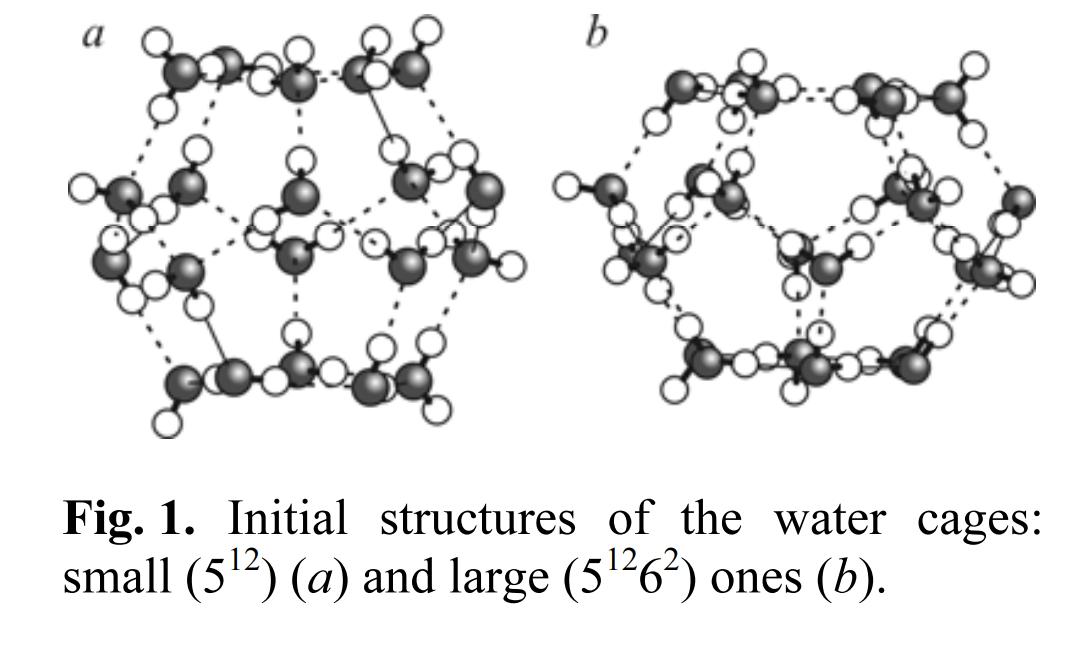
In the present study, we report the results of a systematic investigation of cage-like water structures using the first-principles calculations. These results show that, in the case of methane hydrate, the following nucleation mechanism can be revealed. The formation of small water cavities filled with methane is the first step of the formation of methane hydrate. It is not necessary to occupy all dodecahedral cages by guest molecules. After that small cavities start to form the H-bonding network with surrounding water molecules and a small number of water molecules is enough for the formation of a stable hydrogen-bonding network. The structural information contained in such nuclei is conserved in the forming crystal. Moreover, the presence of a methane molecule between small cages is also important to prevent the adhesion of cavities. It found that the ozone molecule can also stabilize the small cage since the value of the interaction energy between the ozone guest and the water host framework is very close to that obtained for the methane case. However, ozone affects the structure of large cavities and hence, the second guest is necessary to stabilize the hydrate structure.