Boron nitride nanotubes supported icosahedral Pd nanoparticles: Enabling ultrahigh current density-superior hydrogen evolution activity and theoretical insights
-
Authors :
Sada Venkateswarlu, Sooyeon Kim, Mani Balamurugan, Younghu Son, Minyoung Yoon, Ki Tae Nam, Sang Soo Han, Myung Jong Kim
-
Journal :
Applied Catalysis B: Environmental
-
Vol :
345
-
Page :
123609
-
Year :
2024
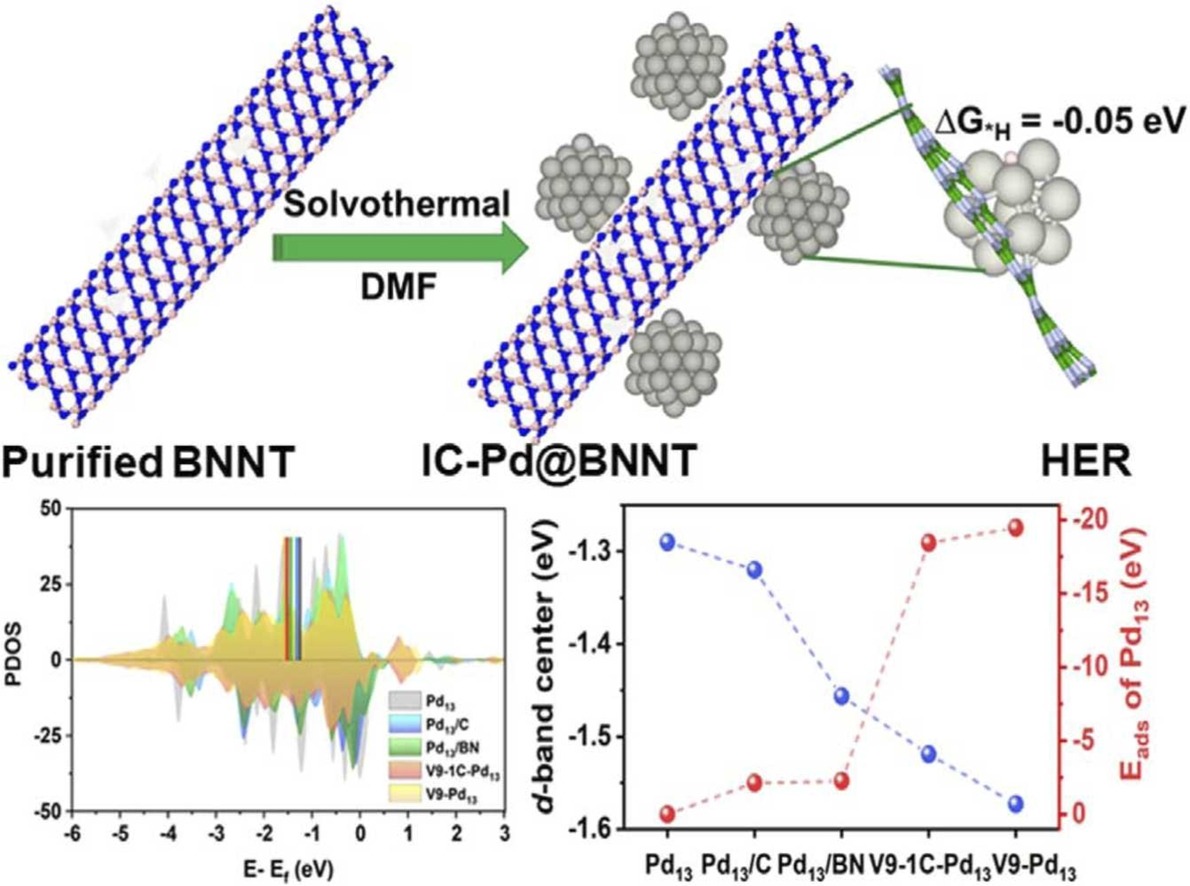
Abstract
An in-situ growth of icosahedral (IC) Pd nanoparticles (NPs) on boron nitride nanotubes (BNNTs) is explored with an external surfactant and reducing agent-free strategy. The IC-Pd@BNNT catalysts show an ultrahigh current density of over − 1000 mA cm−2 with a low overpotential of 199 mV for the hydrogen evolution reaction (HER). At − 20 mA cm−2, the overpotential was as low as 15.7 mV in an acidic medium, which is superior than commercial Pd/C (62.6 mV), and Pt/C (29.4 mV). Moreover, the HER activity of the IC-Pd@BNNT catalysts is maintained even after an accelerated durability test of 40,000 cycles, indicating that the BNNTs are served as a durable support, maintaining the structural integrity of the catalyst. Density functional theory (DFT) calculations confirm that the IC-Pd on the BNNT support with vacancy defects is highly stable and HER active. From the Gas chromatography H2 gas was quantified, and the Faradaic efficiency was achieved to 98.96%.