High-voltage (4.1 V) organic electrode material with an oxygen redox center
-
Authors :
Sechan Lee, Giyun Kwon, Taewon Kang, Jihyeon Kim, Byungju Lee, Chunjoong Kim, Changsoo Lee, Youngsu Kim, Joohyeon Noh, Young-Sang Yu, Dongwhan Lee, Kisuk Kang
-
Journal :
Journal of Materials Chemistry A
-
Vol :
11
-
Page :
22441-22448
-
Year :
2023
Abstract
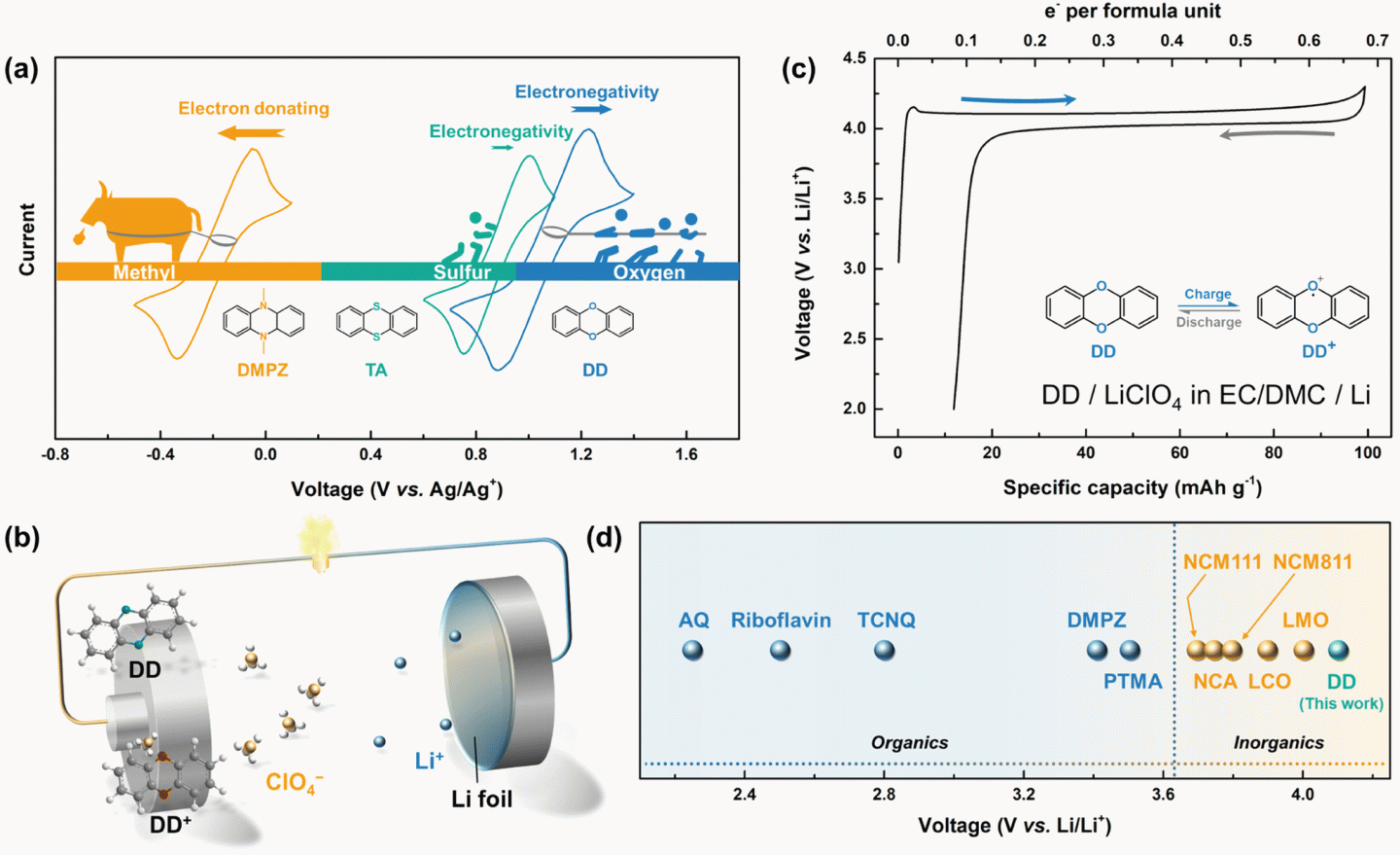
Redox-active organic materials have recently drawn significant attention in the development of green and cost-efficient rechargeable batteries. However, their use as a cathode has been practically hampered in part by the relatively low redox potentials that are typically displayed at ∼2 V (vs. Li/Li+). Herein, we report a rationally designed oxygen-containing heterocyclic compound, dibenzo-1,4-dioxin (DD), which undergoes a reversible redox reaction at the highest redox potential (1.1 V vs. Ag/Ag+ or 4.1 V vs. Li/Li+) among organic electrode materials reported thus far. Moreover, DD, a ready-to-charge active material, delivers a flat discharge voltage profile at this high voltage of 4.1 V in a lithium cell with a respectable rate capability. From a combined spectroscopic and computational analysis, it is revealed that the primary redox reaction takes place via the redox activity of the ring-embedded oxygen based on the p-type reaction in a dual-ion battery. We further demonstrate that introducing an iptycene motif to DD substantially suppresses the dissolution of the electrode material, enhancing the cycle stability without compromising the high discharge voltage. This finding suggests that a practically high discharge voltage over 4 V (vs. Li/Li+) can be achievable from the organic materials by the rational molecular tuning of redox-active atoms and the molecular skeleton, opening up a pathway for developing high-voltage organic batteries.