Anisotropic growth of Pt on Pd nanocube promotes direct synthesis of hydrogen peroxide
-
Authors :
Min-Cheol Kim, Geun-Ho Han, Xiangyun Xiao, Joseph Song, Jaeyoung Hong, Euiyoung Jung, Hong-Kyu Kim, Jae-Pyoung Ahn, Sang Soo Han, Kwan-Young Lee, Taekyung Yu
-
Journal :
Applied Surface Science
-
Vol :
562
-
Page :
150031
-
Year :
2021
Abstract
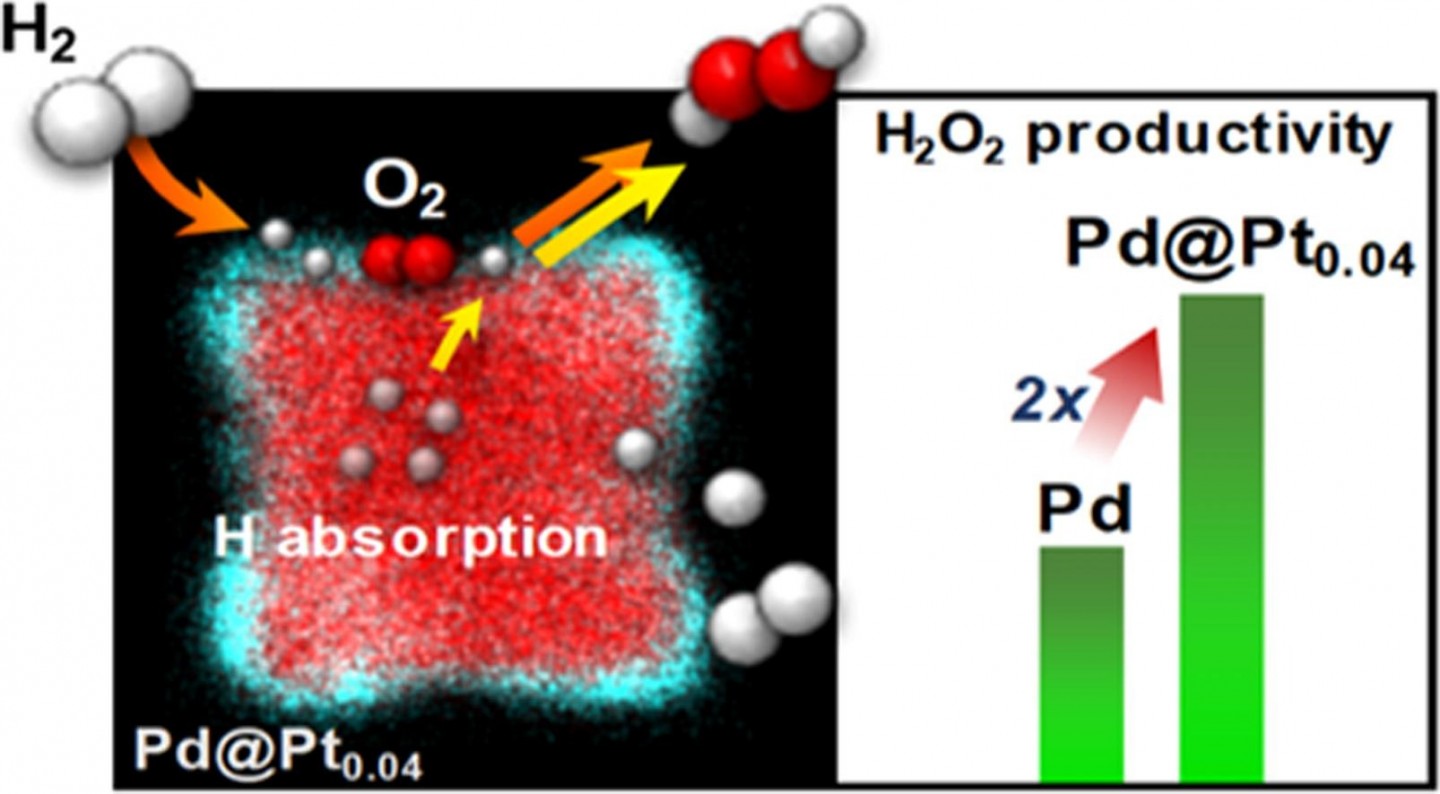
As a joint investigation principle using experimental and theoretical approaches, we report that the anisotropic growth of Pt on Pd nanocubes significantly promotes the direct synthesis of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) from hydrogen (H2) and oxygen (O2). The superior H2O2 productivity of the anisotropic Pd@Pt core@shell nanocrystals results from the enhanced H2 conversion and the H2O2 selectivity compared to Pd and Pt. From the joint investigation, during the anisotropic growth of the Pd@Pt nanocrystals, high-index facets such as (2 1 0) are generated, and they provide numerous active sites for hydrogen dissociation. Notably, even the nano-catalyst is enclosed by Pt shell, the high-index facets are favorable for opening a new route for hydrogen dissolution into the Pd bulk lattices of the Pd@Pt nanocrystals, in which the dissolved hydrogen can react with chemisorbed O2 over the nanocrystals to form H2O2. This mechanism is suggested by a hydrogen temperature programmed reduction (H2-TPR) analysis, in situ transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and density functional theory (DFT) calculations. This study provides another option to improve the catalytic performance of core@shell nanocrystals via the generation of high-index facets through anisotropic growth of nanocrystals, in addition to the well-known strain and charge transfer effects. We expect that the anisotropic growth approach could be extended to other catalytic reactions.