Defect Engineering toward Strong Photocatalysis of Nb-doped Anantase TiO2: Computational Predcitions and Experimental Verifications
슈퍼관리자
2021-05-21
Defect Engineering toward Strong Photocatalysis of Nb-doped Anantase TiO2: Computational Predcitions and Experimental Verifications
-
Authors :
S. Khan, H. Cho, D. Kim, S. S. Han, K. H. Lee, S.-H. Cho, T. Song, and H. Choi
-
Journal :
Applied Catalysis B: Environmental
-
Vol :
206
-
Page :
520-530
-
Year :
2017
Abstract
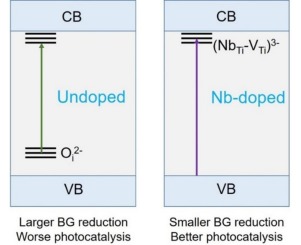
Understanding the roles of point defects in optical transitions is a key to the desirable engineering of photochemical materials. In this study, the origins of the significantly varying optical and photochemical properties of Nb-doped anatase TiO2 were systematically investigated, using density functional theory (DFT) calculations and experimental verifications. We found from DFT calculations that the desirable band gap reduction of anatase TiO2 by ∼0.1 eV reported in many of experimental reports and the resultant improvements of photocatalytic and photovoltaic efficiencies of Nb5+-doped anatase TiO2 are due to the formation of complex (NbTi-VTi)3− as the compensator of NbTi+. Our experiments demonstrated that the O2-rich annealing, which is expected to increase the concentration of desirable (NbTi-VTi)3− complex, narrows band gap of TiO2 and strongly enhances the photocatalytic activity of Nb-doped TiO2 particle. On the contrary, pure TiO2 showed rather worse photocatalytic performances when annealed in O2-rich atmosphere, which is due to the formation of deep level by O-interstitial defect (Oi). Theoretically obtained charge effective masses could further explain the different photocatalytic activities of undoped and Nb-doped TiO2.