Effect of Shuttling Catalyst on the Migration of Hydrogen Adatoms: A Strategy for the Facile Hydrogenation of Graphene
슈퍼관리자
2021-05-21
Effect of Shuttling Catalyst on the Migration of Hydrogen Adatoms: A Strategy for the Facile Hydrogenation of Graphene
-
Authors :
S. S. Han, H. Kim, and N. Park
-
Journal :
Journal of Physical Chemistry C
-
Vol :
115
-
Page :
24696-24701
-
Year :
2011
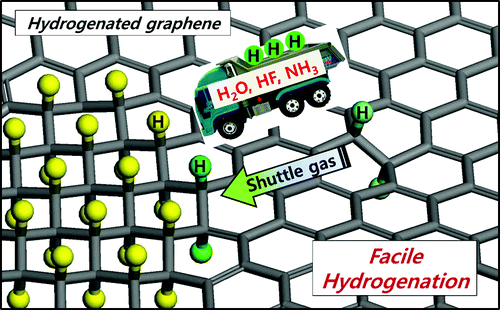
Abstract
Using density functional theory calculations, we have investigated a strategy for the facile hydrogenation of graphene. We show that the presence of polar hydride molecules, such as H2O, HF, and NH3 (physisorbed molecules that mediate/assist the migration of atomic H adatoms on graphene, named “shuttle gases” in the present work), can provide a favorable catalytic effect (lowering the H migration barrier) and a favorable thermodynamic effect (activating the direct transition to the second-nearest-neighbor site). In comparison with the widely known fact that the migration of chemisorbed H is kinetically unfavorable on graphene, this mechanism for shuttling catalysis provides an easier migration channel. We propose that randomly distributed hydrogen adatoms on graphene can transform into a compactly aggregated hydrogenation domain (similar to graphane, as suggested in the literature) by heat treatment in the presence of a shuttling catalyst.