Balance in Adsorption Energy of Reactants Steers CO Oxidation Mechanism of Ag13 and Ag12Pd1 Nanoparticles: Association Mechanism versus Carbonate Mediated Mechanism
슈퍼관리자
2021-05-21
Balance in Adsorption Energy of Reactants Steers CO Oxidation Mechanism of Ag13 and Ag12Pd1 Nanoparticles: Association Mechanism versus Carbonate Mediated Mechanism
-
Authors :
H. Y. Kim, S. S. Han, J. H. Ryu, and H. M. Lee
-
Journal :
Journal of Physical Chemistry C
-
Vol :
114
-
Page :
3156-3160
-
Year :
2010
Abstract
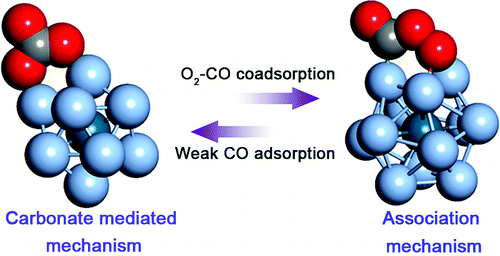
CO oxidation is a very useful reference reaction in catalysis by nanoparticles (NPs). Two reaction modelssanassociation mechanism (AM) and a carbonate-mediated mechanism (CMM)shave been suggested for CO
oxidation catalyzed by small NPs. It is still unclear, however, when and why these mechanisms preferentially
operate. With the Ag13 crystalline NPs and the Ag12Pd1 core-shell NP, using a density functional theory
calculation and a microkinetic reaction model, we found that the different reaction mechanisms can operate
with different reaction intermediates accompanied by a balance in the adsorption energy of reactants. Variations
in the adsorption energy of adsorbates can result from the interchange of two reaction mechanisms, even in
a single NP. An AM operates when both reactants interact strongly with a NP, whereas the contribution of
the CMM in CO oxidation increases when a CO molecule interacts weakly or not at all with a NP.