Adsorption Mechanism and Uptake of Methane in Covalent-Organic Frameworks: Theory and Experiment
슈퍼관리자
2021-05-21
Adsorption Mechanism and Uptake of Methane in Covalent-Organic Frameworks: Theory and Experiment
-
Authors :
J. L. Mendoza-Cort
-
Journal :
Journal of Physical Chemistry A
-
Vol :
114
-
Page :
10824-10833
-
Year :
2010
Abstract
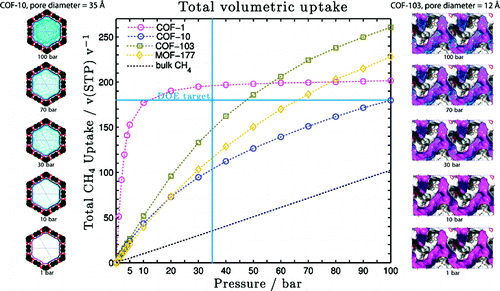
ond order Møller−Plesset (MP2) perturbation theory using doubly polarized quadruple-ζ (QZVPP) basis sets]. This FF was validated by comparison with the equation of state for CH4 and by comparison with the experimental uptake isotherms at 298 K (reported here for COF-5 and COF-8), which agrees well (within 2% for 1−100 bar) with the GCMC simulations. From our simulations we have been able to observe, for the first time, multilayer formation coexisting with a pore filling mechanism. The best COF in terms of total volume of CH4 per unit volume COF absorbent is COF-1, which can store 195 v/v at 298 K and 30 bar, exceeding the U.S. Department of Energy target for CH4 storage of 180 v/v at 298 K and 35 bar. The best COFs on a delivery amount basis (volume adsorbed from 5 to 100 bar) are COF-102 and COF-103 with values of 230 and 234 v(STP: 298 K, 1.01 bar)/v, respectively, making these promising materials for practical methane storage.