Cooperative Carbon Dioxide Capture in Diamine-Appended Magnesium–Olsalazine Frameworks
-
Authors :
Ziting Zhu, Surya T. Parker, Alexander C. Forse, Jung-Hoon Lee, Rebecca L. Siegelman, Phillip J. Milner, Hsinhan Tsai, Mengshan Ye, Shuoyan Xiong, Maria V. Paley, Adam A. Uliana, Julia Oktawiec, Bhavish Dinakar, Stephanie A. Didas, Katie R. Meihaus, Jeffrey A. Reimer, Jeffrey B. Neaton, and Jeffrey R. Long
-
Journal :
Journal of the American Chemical Society
-
Vol :
145
-
Page :
17151–17163
-
Year :
2023
Abstract
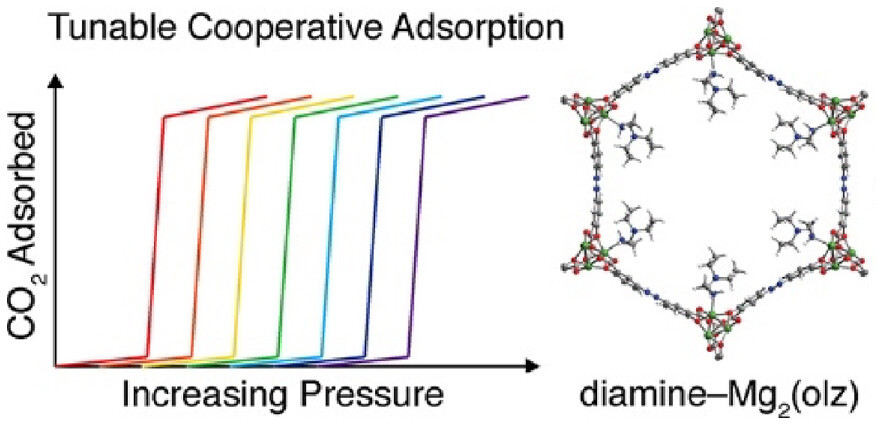
Diamine-appended Mg2(dobpdc) (dobpdc4– = 4,4′-dioxidobiphenyl-3,3′-dicarboxylate) metal–organic frameworks have emerged as promising candidates for carbon capture owing to their exceptional CO2 selectivities, high separation capacities, and step-shaped adsorption profiles, which arise from a unique cooperative adsorption mechanism resulting in the formation of ammonium carbamate chains. Materials appended with primary,secondary-diamines featuring bulky substituents, in particular, exhibit excellent stabilities and CO2 adsorption properties. However, these frameworks display double-step adsorption behavior arising from steric repulsion between ammonium carbamates, which ultimately results in increased regeneration energies. Herein, we report frameworks of the type diamine–Mg2(olz) (olz4– = (E)-5,5′-(diazene-1,2-diyl)bis(2-oxidobenzoate)) that feature diverse diamines with bulky substituents and display desirable single-step CO2 adsorption across a wide range of pressures and temperatures. Analysis of CO2 adsorption data reveals that the basicity of the pore-dwelling amine─in addition to its steric bulk─is an important factor influencing adsorption step pressure; furthermore, the amine steric bulk is found to be inversely correlated with the degree of cooperativity in CO2 uptake. One material, ee-2–Mg2(olz) (ee-2 = N,N-diethylethylenediamine), adsorbs >90% of the CO2 from a simulated coal flue stream and exhibits exceptional thermal and oxidative stability over the course of extensive adsorption/desorption cycling, placing it among top-performing adsorbents to date for CO2 capture from a coal flue gas. Spectroscopic characterization and van der Waals-corrected density functional theory calculations indicate that diamine–Mg2(olz) materials capture CO2 via the formation of ammonium carbamate chains. These results point more broadly to the opportunity for fundamentally advancing materials in this class through judicious design.